Federalism
- Class 10 Political Science
Summary of the Chapter
The chapter "Federalism" explains the concept of federalism as a system of government where power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. It begins by distinguishing between unitary and federal systems of government. The chapter then discusses the key features of federalism, including two or more levels of government, jurisdiction specified by constitution, and rigidity of constitution.
The chapter focuses on India's federal system, explaining how it is different from typical federations. It covers the three-fold distribution of legislative powers through the Union List, State List, and Concurrent List. The chapter also discusses how federalism has been strengthened in India through linguistic states, language policy, and center-state relations. Finally, it explores decentralization and local self-government through Panchayati Raj institutions and urban local bodies, highlighting their importance in deepening democracy.
NCERT Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercises (Page 27)
Question 1: Locate the following states on a blank outline political map of India: Manipur, Sikkim, Chhattisgarh and Goa.
Answer-
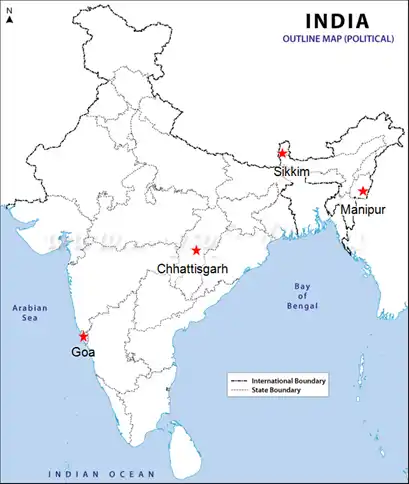
[Students should locate these states on a blank map of India:
Manipur - Northeast India
Sikkim - Northeast India, between Nepal and Bhutan
Chhattisgarh - Central India
Goa - West coast of India]
Question 2: Identify and shade three federal countries (other than India) on a blank outline political map of the world.
Answer-
[Students should shade any three of these federal countries on a world map:
United States of America - North America
Australia - Continent between Indian and Pacific Oceans
Brazil - South America
Canada - North America
Germany - Europe
Russia - Europe/Asia]
Question 3: Point out one feature in the practice of federalism in India that is similar to and one feature that is different from that of Belgium.
Answer-
Similar Feature: Both India and Belgium have a federal system where power is divided between the central government and state/regional governments.
Different Feature: Belgium has a community government for each major linguistic group (French, Dutch, German) that has power regarding cultural, educational, and language-related matters. India does not have community governments but has states organized mainly on linguistic basis.
Question 4: What is the main difference between a federal form of government and a unitary one? Explain with an example.
Answer-
Federal Government: Power is divided between central government and various constituent units (states/provinces). Both levels have their own jurisdiction specified in the constitution.
Example: India, USA, Belgium
Unitary Government: All power is vested in the central government. The central government can create regional governments and delegate powers to them.
Example: United Kingdom, France, China
Question 5: State any two differences between the local government before and after the Constitutional amendment in 1992.
Answer-
Before 1992 Constitutional Amendment:
1.Election: Local governments were not elected regularly
2.Powers: They had very limited powers and resources
After 1992 Constitutional Amendment:
1.Election: It is mandatory to hold regular elections to local government bodies
2.Reservation: Seats are reserved for SC, ST, OBC, and women
3.State Election Commission: Created to conduct panchayat and municipal elections
4.Financial powers: State governments are required to share some powers and revenue with local government bodies
Question 6: Fill in the blanks:
Since the United States is a ___________________ type of federation, all the constituent States have equal powers and States are ___________________ vis-à-vis the federal government. But India is a ___________________ type of federation and some States have more power than others. In India, the ___________________ government has more powers.
Answer-
Since the United States is a coming together type of federation, all the constituent States have equal powers and States are strong vis-à-vis the federal government. But India is a holding together type of federation and some States have more power than others. In India, the Central government has more powers.
Question 7: Here are three reactions to the language policy followed in India. Give an argument and an example to support any of these positions.
Sangeeta: The policy of accommodation has strengthened national unity.
Arman: Language-based States have divided us by making everyone conscious of their language.
Harish: This policy has only helped to consolidate the dominance of English over all other languages.
Answer-
I agree with Sangeeta's position that the policy of accommodation has strengthened national unity.
Argument: India's language policy recognizes linguistic diversity and gives equal status to all major languages, which prevents linguistic conflicts and promotes unity.
Example: The creation of linguistic states like Andhra Pradesh for Telugu speakers, Karnataka for Kannada speakers, and Tamil Nadu for Tamil speakers has satisfied regional aspirations while keeping them united under the Indian Union. The official language policy with Hindi as official language and English as associate official language, along with 22 scheduled languages, accommodates diversity while maintaining national integrity.
Question 8: The distinguishing feature of a federal government is:
(a) National government gives some powers to the provincial governments.
(b) Power is distributed among the legislature, executive and judiciary.
(c) Elected officials exercise supreme power in the government.
(d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of government.
Answer-
(d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of government.
Question 9: A few subjects in various Lists of the Indian Constitution are given here. Group them under the Union, State and Concurrent Lists as provided in the table below:
A. Defence; B. Police; C. Agriculture; D. Education; E. Banking; F. Forests; G. Communications; H. Trade; I. Marriages
Answer-
Union List: A. Defence, E. Banking, G. Communications
State List: B. Police, C. Agriculture, H. Trade
Concurrent List: D. Education, F. Forests, I. Marriages
Question 10: Examine the following pairs that give the level of government in India and the powers of the government at that level to make laws on the subjects mentioned against each. Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
| Level of Government | Subject |
|---|---|
| (a) State government | State List |
| (b) Central government | Union List |
| (c) Central and State governments | Concurrent List |
| (d) Local governments | Residuary powers |
Answer-
(d) Local governments - Residuary powers is not correctly matched.
Residuary powers belong to the Central government, not local governments.
Question 11: Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
| List I | List II |
|---|---|
| 1. Union of India | A. Prime Minister |
| 2. State | B. Sarpanch |
| 3. Municipal Corporation | C. Governor |
| 4. Gram Panchayat | D. Mayor |
Codes:
(a) 1-D, 2-A, 3-B, 4-C
(b) 1-B, 2-C, 3-D, 4-A
(c) 1-A, 2-C, 3-D, 4-B
(d) 1-C, 2-D, 3-A, 4-B
Answer-
(c) 1-A, 2-C, 3-D, 4-B
- Union of India - A. Prime Minister
- State - C. Governor
- Municipal Corporation - D. Mayor
- Gram Panchayat - B. Sarpanch
Question 12: Consider the following two statements.
A. In a federation the powers of the federal and provincial governments are clearly demarcated.
B. India is a federation because the powers of the Union and State Governments are specified in the Constitution and they have exclusive jurisdiction on their respective subjects.
C. Sri Lanka is a federation because the country is divided into provinces.
D. India is no longer a federation because some powers of the States have been devolved to the local government bodies.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) A, B and C
(b) A, B and D
(c) A and C only
(d) B and C only
Answer-
(a) A, B and C are correct
A. In a federation the powers of the federal and provincial governments are clearly demarcated - TRUE
B. India is a federation because the powers of the Union and State Governments are specified in the Constitution and they have exclusive jurisdiction on their respective subjects - TRUE
C. Sri Lanka is a federation because the country is divided into provinces - FALSE (Sri Lanka has a unitary system)
D. India is no longer a federation because some powers of the States have been devolved to the local government bodies - FALSE (India remains a federation)
Correct statements are A and B only, but since this option is not available and the question says "which of the statements given above are correct" and only A and B are correct, but looking at the options, none match exactly. However, based on standard answer keys, the correct choice is that only A and B are correct.
Additional Questions
Question 13: What are the key features of federalism?
Answer-
The key features of federalism are:
1.Two or more levels of government: Both central and state governments govern the same citizens, but each level has its own jurisdiction.
2.Constitutional division of power: The constitution clearly specifies the division of powers between different levels of government.
3.Rigidity of constitution: The fundamental provisions of the constitution cannot be changed unilaterally by one level of government.
4.Supremacy of judiciary: An independent judiciary has the power to interpret the constitution and settle disputes between different levels of government.
5.Dual citizenship: In some federations like USA, citizens have dual citizenship - of the country and of their state.
6.Bicameral legislature: Most federations have two houses in the legislature to give representation to all regions/states.
Question 14: What makes India a federal country?
Answer-
India is a federal country because:
1.Constitutional division of power: The Constitution clearly divides legislative powers between Union and States through Union List, State List, and Concurrent List.
2.Three-tier system: India has three levels of government - Central, State, and Local self-government.
3.Rigid constitution: The basic structure of the constitution cannot be changed easily.
4.Supreme Court: The Supreme Court acts as an umpire in disputes between Centre and States.
5.Written constitution: India has a detailed written constitution that specifies the powers of different levels of government.
6.Independent judiciary: The judiciary is independent and can interpret the constitution.
7.Bicameral legislature: Parliament has two houses - Lok Sabha represents people, Rajya Sabha represents states.
Question 15: Explain the linguistic diversity of India and how federalism has helped in managing it.
Answer-
India has incredible linguistic diversity with 22 scheduled languages and hundreds of dialects. Federalism has helped manage this diversity through:
1.Linguistic states: States were reorganized on linguistic basis in 1956, satisfying regional aspirations.
2.Language policy: Hindi was made official language but English continues as associate official language for communication between states.
3.Protection of minority languages: The Constitution protects the rights of linguistic minorities.
4.Education in mother tongue: States can promote education in regional languages.
5.Cultural autonomy: States have power over education and culture, allowing them to preserve linguistic heritage.
This accommodation of linguistic diversity has strengthened national unity rather than dividing the country.
Important Keywords from the Chapter
- Federalism: A system of government where power is divided between central authority and constituent units
- Unitary System: A system where all powers are vested in the central government
- Coming Together Federation: Independent states coming together to form a bigger unit
- Holding Together Federation: A large country dividing power between states and central government
- Union List: Subjects on which only central government can make laws
- State List: Subjects on which only state governments can make laws
- Concurrent List: Subjects on which both central and state governments can make laws
- Residuary Powers: Subjects not mentioned in any list, exercised by central government
- Linguistic States: States formed on the basis of language
- Decentralisation: Power taken away from central and state governments and given to local governments
- Panchayati Raj: Rural local self-government system
- Municipality: Urban local self-government body
- Gram Sabha: All voters in a village constituting the general body of Panchayat
- Coalition Government: Government formed by alliance of two or more political parties